Site
http://www.hhmi.org/scientists/linda-b-buck
https://www.facebook.com/Linda-B-Buck-121245494613130/info?tab=page_info
Biography
Linda Brown Buck (born January 29, 1947), is an American biologist best known for her work on the olfactory system. She was awarded the 2004 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, along with Richard Axel, for their work on olfactory receptors. She is currently on the faculty of the Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center in Seattle.
Apple pie baking in the oven, newly mowed grass, sulfur emanating from Fourth of July fireworks—these are just a few of the 10,000 or more distinct odors our noses can detect. Linda Buck studies exactly how odor molecules in the environment are detected by specialized receptors in the nose and then translated by the brain into specific smells. Her groundbreaking research has provided important insights into the mechanisms underlying the sense of smell. And it is for this work that Buck and fellow HHMI investigator Richard Axel won the 2004 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
Buck first became interested in odor recognition in the late 1980s, when little was known about how odors are detected or how the nervous system translates various odor molecules into perceived smells. "To me, this was a monumental problem and a wonderful puzzle. I was hooked," Buck recalled.
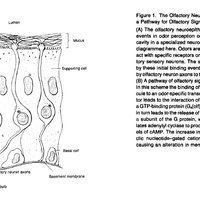
At that time, olfactory receptors had not yet been discovered. Buck set out to find them. Working as a postdoctoral fellow in Axel's laboratory at Columbia University, she put in 15 hour days for several years before she and Axel found precisely what they were looking for—a family of some 1,000 genes that encode odor receptors located in the lining of the nose.
Buck then used the odor receptor genes as tools to unravel how the identities of different odors are encoded at the molecular level and in the brain to produce the perception of distinct odors. In later studies, she and her colleagues uncovered sensory maps in the olfactory bulb that are virtually identical in different individuals. They also discovered that the sense of smell in mammals relies on a combinatorial approach to recognizing and processing odors. Thus, rather than a specific odor being detected by an individual receptor, the olfactory system uses varying combinations of receptors to produce distinct smells.
Buck continues to be fascinated by the inner workings of the olfactory system, an enthusiasm she hopes to convey to the graduate students and postdoctoral fellows in her lab. "I tell them that it is absolutely essential to work on something that fascinates them and that they are excited about," Buck said.